This video provides a detailed explanation of the definition of current electricity, including the time rate of flow of charge, the net charge, and the direction of current.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
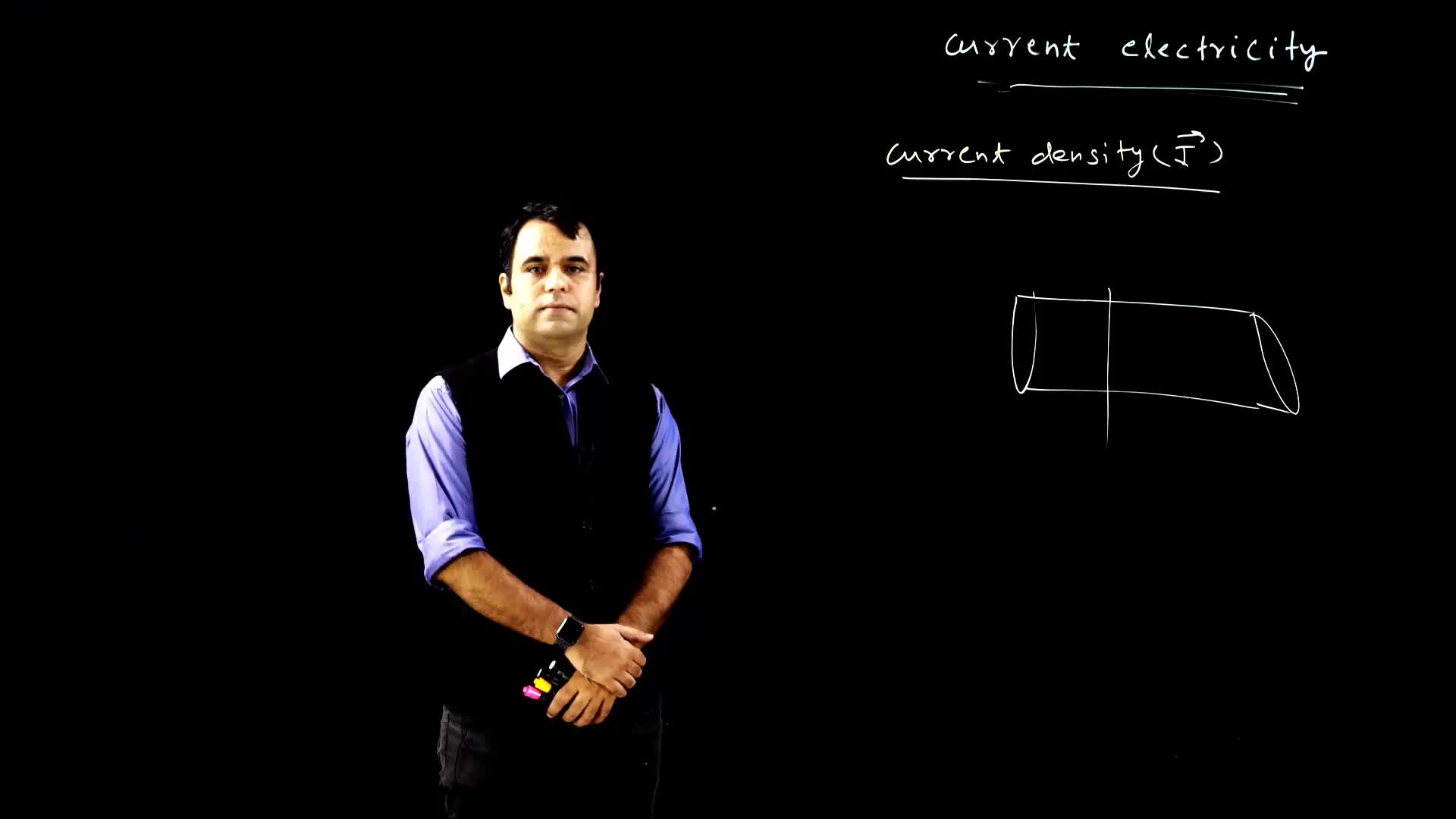
This video explains the concept of current density, which is a vector quantity defined by J and represents the current flow through a cross-sectional area. The video discusses the calculation of current density in the direction of current flow, taking into account the component of area and the angle between the area vector and current direction.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
The video explains the concept of drift velocity in conductors. It starts by discussing the motion of free electrons in a conductor with no external source, then delves into the effects of an external source like a battery on the electrons, and concludes with the calculation of drift velocity and mean free path.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
This video provides an explanation of Kirchhoff's first law and its application in complex circuits. The law is based on the conservation of charge and states that the algebraic sum of currents at any junction in a circuit is always zero. The video provides a detailed explanation of how to derive and apply this law in circuit analysis.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
The video explains Kirchhoff's Second Law, which is based on conservation of energy in an electrical circuit. It discusses the movement of electrons, potential difference, and the calculation of potential difference in a closed loop.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
This video explains the concept of Ohm's Law, which is the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a conductor. It delves into the application of Ohm's Law, relationship between resistance and resistivity, and the conditions under which the formula for resistance is valid.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
The video explains how to calculate the potential change across a real battery, considering its internal resistance. It discusses the potential change for charging and discharging the battery, the effect of direction of current, and the implications for applying Kirchhoff's law. It advises against memorizing formulas and emphasizes separate calculation for the ideal portion of the battery and the internal resistance.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
This video explains how to calculate the potential change across resistance and ideal batteries in electrical circuits.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
The video discusses the properties of electric current, including its scalar nature, calculation in linear and circular conductors, and the use of electron movement around a nucleus to calculate current.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
The video discusses how the resistance and resistivity of a conductor change with temperature. It explains the relationship between resistance, resistivity, and temperature, as well as the formula for calculating resistivity and resistance as a function of temperature.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||