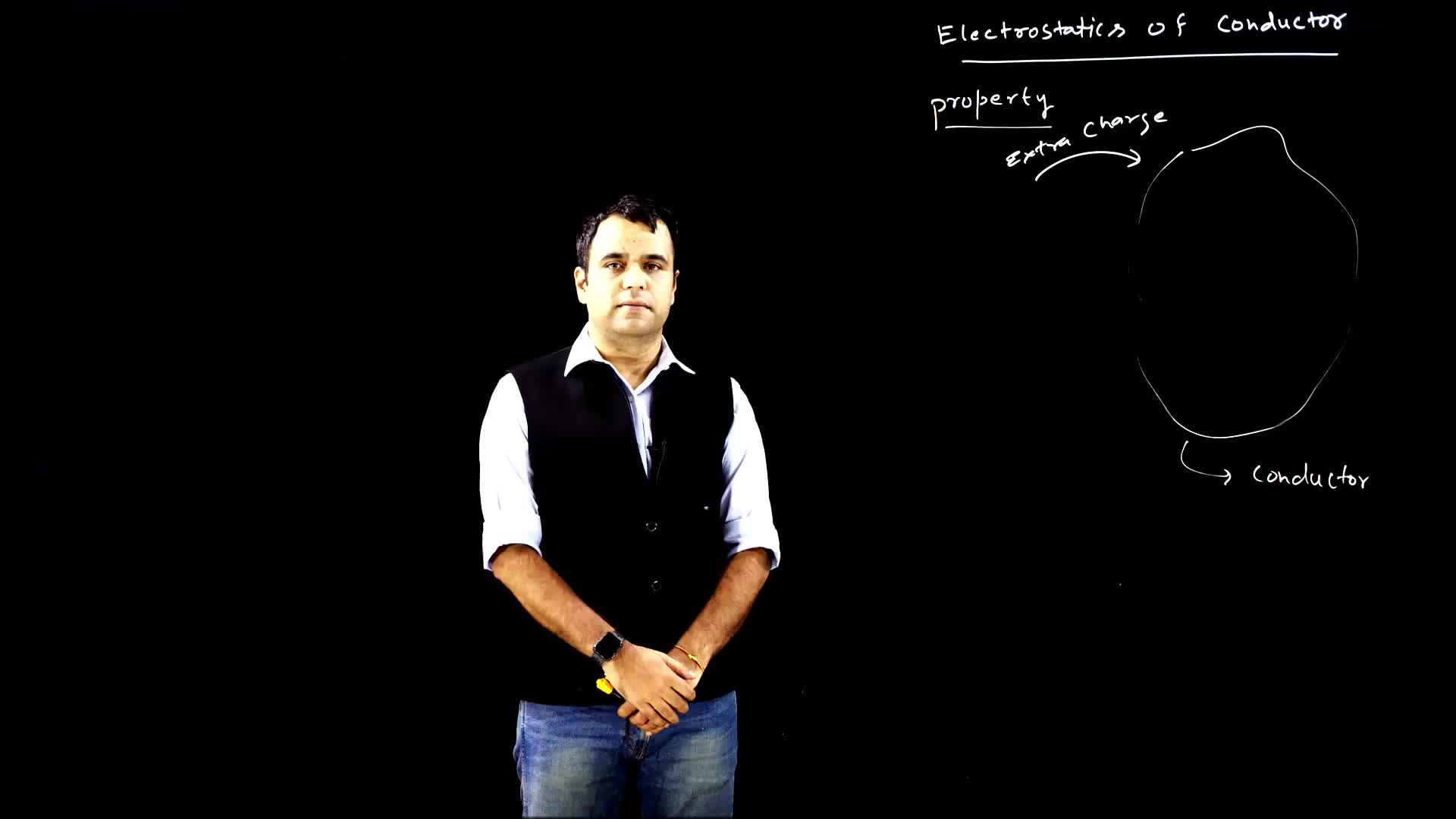
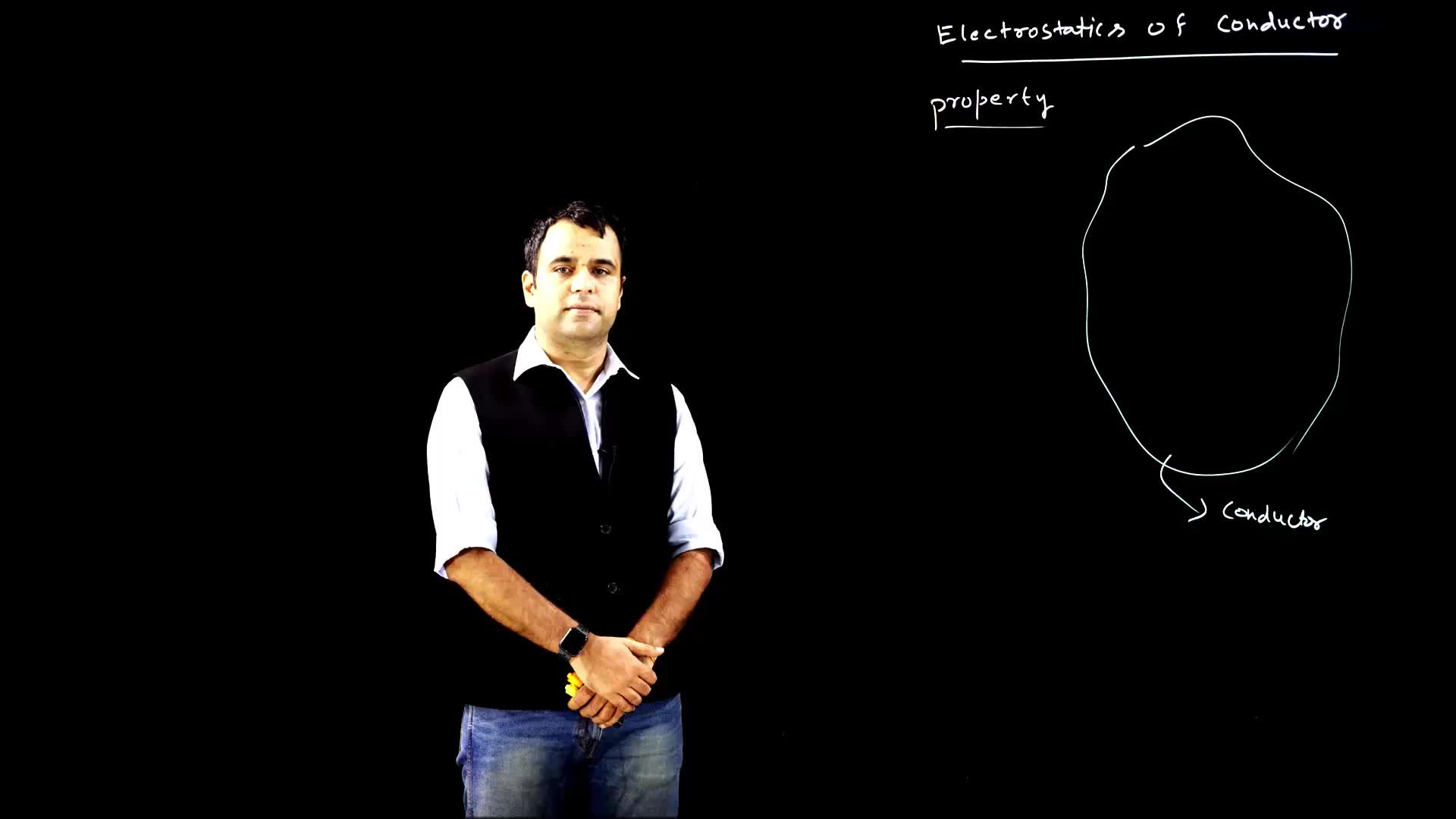
This video discusses the property of conductors in relation to the distribution of extra charges provided to the conductor. It explains how the extra charges always reside on the surface of the conductor after achieving equilibrium, due to the relationship between potential energy and distance.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
The video explains the calculation of the potential due to a dipole along its perpendicular bisector, using equations and derivations to show that the potential along the perpendicular bisector of the dipole is zero.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
The video discusses the calculation of potential along the axis of a dipole, explaining the formula and steps involved in the process.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
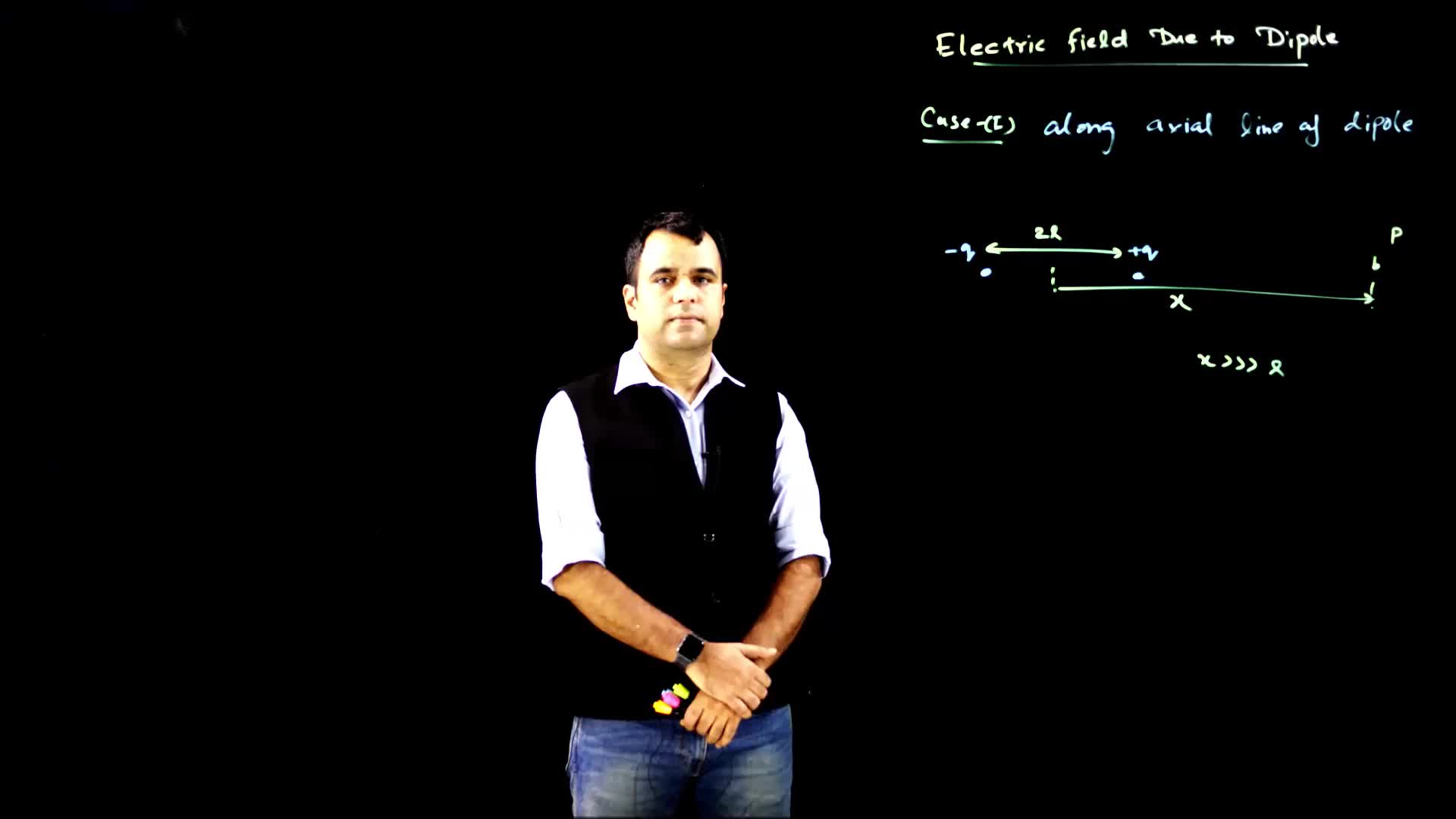
This video explains how to calculate the electric field at a general location due to a dipole. It covers the components of the electric field, formulas for calculating the field components, and the angle of the net electric field with the position vector.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
The video explains how to calculate the electric field due to a dipole along the perpendicular bisector of the dipole. The presenter discusses the process step by step and provides equations for the calculation.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
Derivation of the formula for electric field along the axial line of a dipole using the binomial expansion.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
This video discusses the concept of equipotential surfaces, which are defined as the locus of all points having the same potential. The video then explains the properties of equipotential surfaces and how they are drawn for different scenarios.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
The video explains the relationship between charge density, electric fields, and conductors. It discusses the concept of sigma as the charge density onto the conductor and how to calculate the electric field very nearby to the conductor using the formula sigma upon epsilon naught.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
Explanation of the behavior of electric fields inside cavities of conductors, including the influence of charge and symmetry on electric field strength.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
This video explains the concept of electric field in conductors, focusing on the behavior of the electric field inside and outside a conductor. It discusses how the redistribution of charges in response to an external electric field affects the electric field both inside and outside the conductor.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
This video discusses the calculation of the electric field due to a uniformly charged non-conducting sphere, both for inside and outside points. It covers the derivation of the electric field formulas and discusses the variations of the electric field based on the distance from the center of the sphere.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
This video discusses the property of a conductor where the potential inside the conductor is always the same, and provides a mathematical proof for this. It also explains how this property is related to the equilibrium state and the movement of electrons.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
This video discusses the electrostatics of conductors, focusing on the properties of the electric field inside the conductor and the conditions for achieving equilibrium. The main property discussed is that the electric field inside a conductor is always zero when in equilibrium.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
An explanation of the concept of an electric dipole and dipole moment, and the reasons for studying them in the context of atoms and materials.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
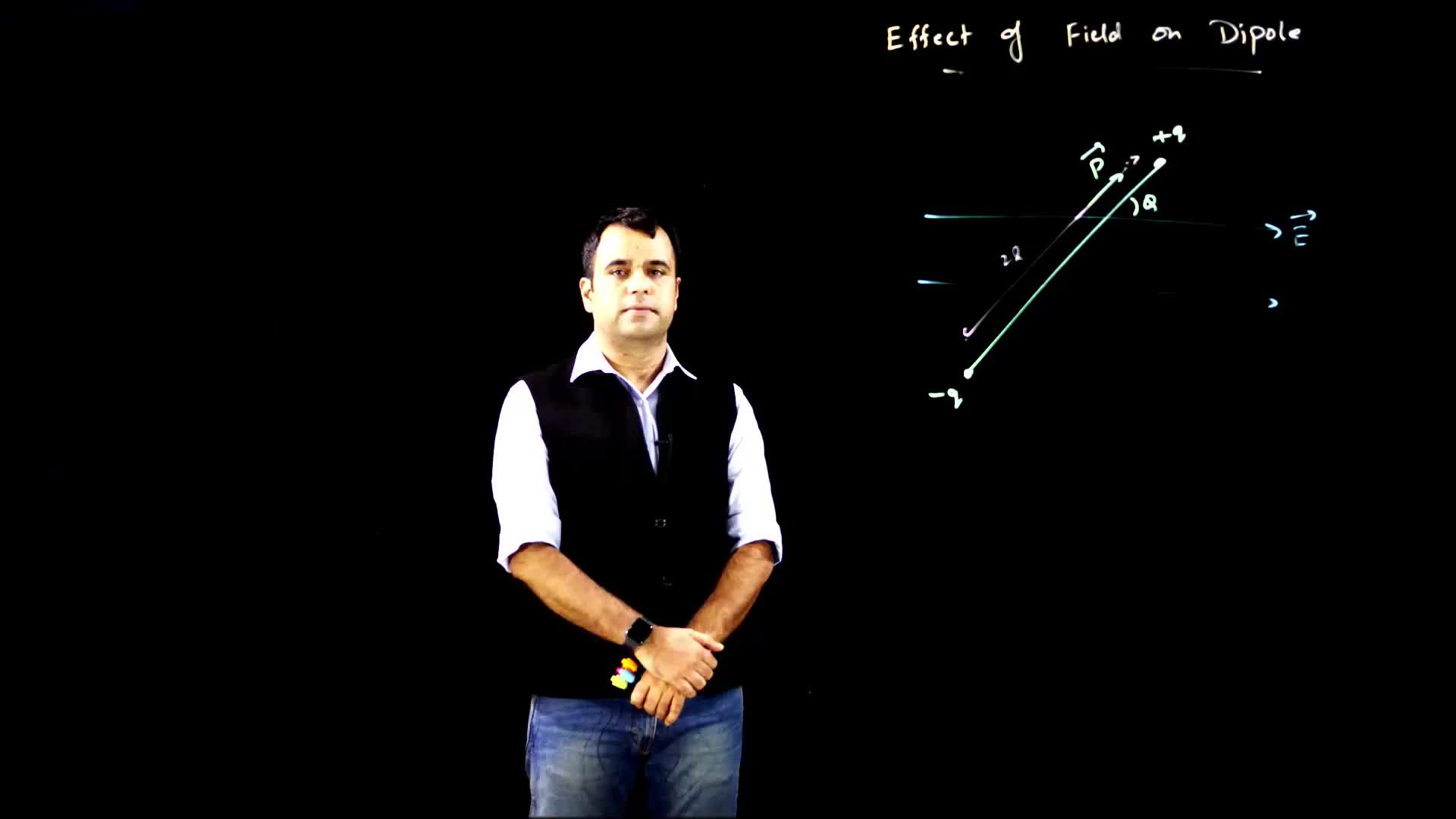
This video explains the effects of placing a dipole in an external electric field, including the forces and torques experienced by the dipole, as well as the change in potential energy. It also discusses the relationship between potential energy and torque, and the formula for absolute potential energy.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
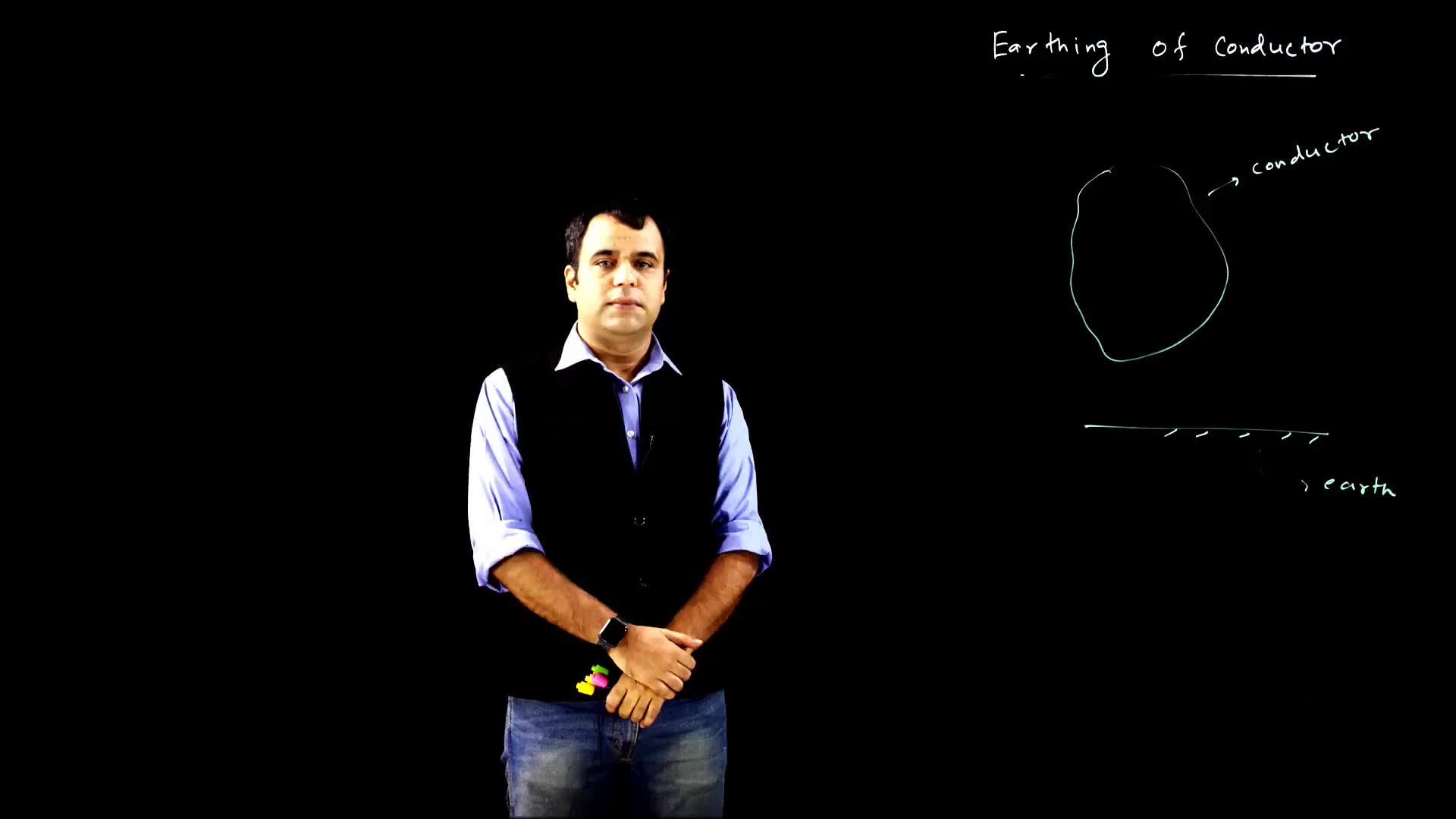
This video explains the concept of what happens when a conductor is connected to the Earth, and how the potential of the conductor becomes zero. The potential of the Earth remains constant due to its large size, and the flow of charge occurs until both bodies reach the same potential.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
This video explains the charge distribution on a multiple plate system. It covers the calculation of small Q and Q dash based on Q1 and Q2, the relationship between electric field and charge distribution, and the distribution of charge onto the plates.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
The video discusses how charge gets distributed on a metallic plate when a positive charge is applied. It explores the relationship between the charges on each side of the plate and the electric fields experienced at a point inside the plate.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
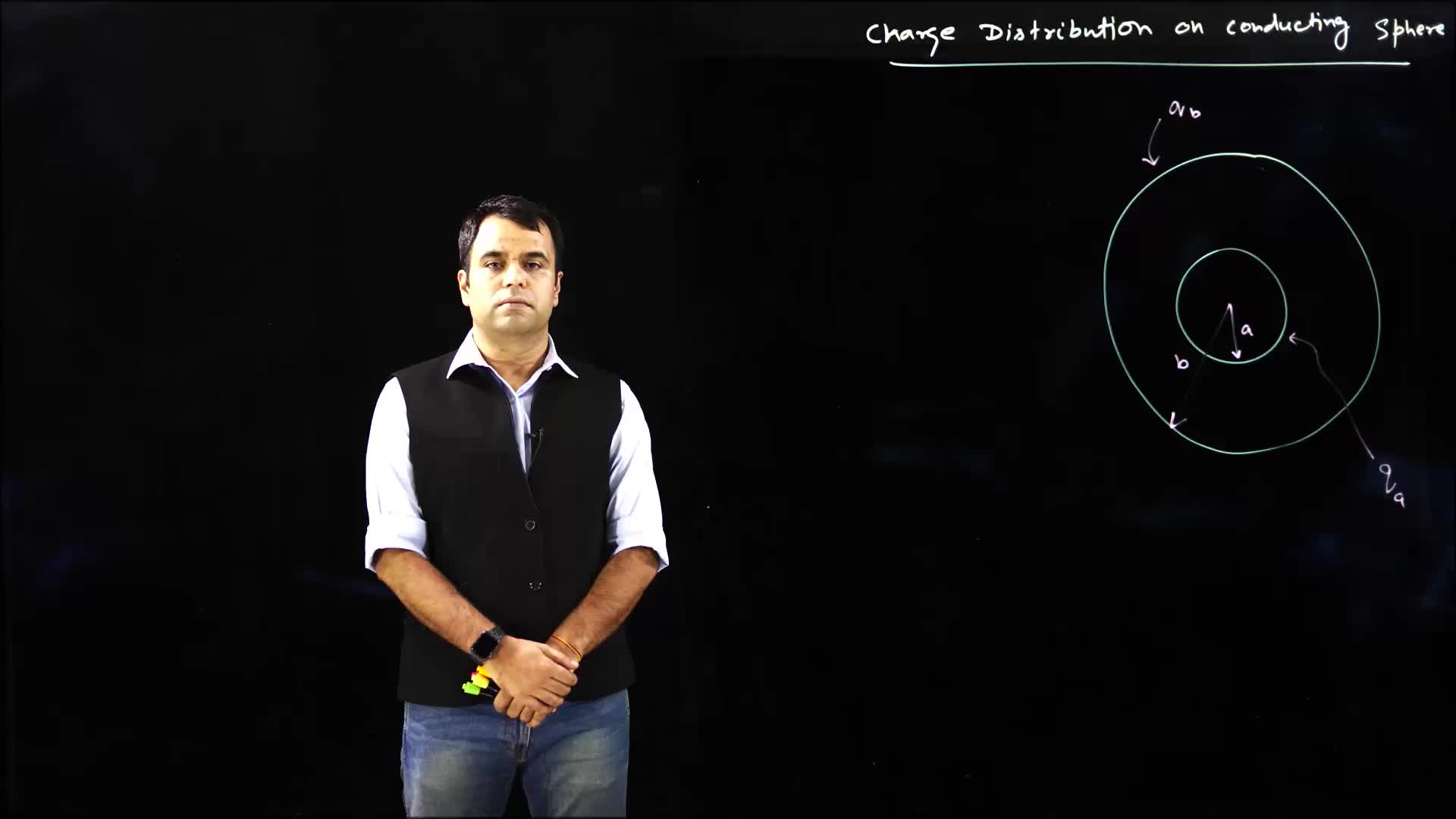
The video explains how charge is distributed on the inner and outer surfaces of concentric spherical shells, as well as the application of Gauss's law to calculate the charge distribution.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||
This video explains the calculation of potential due to a uniformly charged non conducting sphere. It covers the formulas for potential for both outside and inside points, the relationship between potential and electric field, and the importance of non conducting solid spheres in these calculations.
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:00 |
|
|
|
|
0:05 | ||
|
|
0:10 |
|
|
|
|
0:15 | ||
|
|
0:20 | ||
|
|
0:25 |
|
|
|
|
0:30 | ||